doCreateBean方法
上文Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上),分析了单例的Bean初始化流程,并跟踪代码进入了主流程,看到了Bean是如何被实例化出来的。先贴一下AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean方法代码:
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
下面继续分析初始化一个Bean的流程,不太重要的流程就跳过了。
属性注入
属性注入的代码比较好找,可以看一下40行,取名为populateBean,即填充Bean的意思,看一下代码实现:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
这段代码层次有点深,跟一下74行的applyPropertyValues方法,最后那个pvs的实现类为MutablePropertyValues,里面持有一个List<PropertyValue>,每一个PropertyValue包含了此Bean属性的属性名与属性值。74行的代码实现为:
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs == null || pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (System.getSecurityManager()!= null) {
if (bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
}
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
之后在第41行~第76行做了一次深拷贝(只是名字叫做深拷贝而已,其实就是遍历PropertyValue然后一个一个赋值到一个新的List而不是Java语义上的Clone,这里使用深拷贝是为了解析Values值中的所有引用),将PropertyValue一个一个赋值到一个新的List里面去,起名为deepCopy。最后执行83行进行复制,bw即BeanWrapper,持有Bean实例的一个Bean包装类,看一下代码实现:
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
// here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
// We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new LinkedList<PropertyAccessException>();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception.
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray =
propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[propertyAccessExceptions.size()]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
}
这段代码没什么特别的,遍历前面的deepCopy,拿每一个PropertyValue,执行第12行的setPropertyValue:
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
PropertyTokenHolder tokens = (PropertyTokenHolder) pv.resolvedTokens;
if (tokens == null) {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
BeanWrapperImpl nestedBw;
try {
nestedBw = getBeanWrapperForPropertyPath(propertyName);
}
catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) {
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Nested property in path '" + propertyName + "' does not exist", ex);
}
tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedBw, propertyName));
if (nestedBw == this) {
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens;
}
nestedBw.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
else {
setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
}
找一个合适的BeanWrapper,这里就是自身,然后执行17行的setPropertyValue方法进入最后一步,方法非常长,截取核心的一段:
final Method writeMethod = (pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
pd.getWriteMethod());
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()) && !writeMethod.isAccessible()) {
if (System.getSecurityManager()!= null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
else {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
}
final Object value = valueToApply;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
writeMethod.invoke(object, value);
return null;
}
}, acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
writeMethod.invoke(this.object, value);
}
大致流程就是两步:
(1)拿到写方法并将方法的可见性设置为true
(2)拿到Value值,对Bean通过反射调用写方法
这样完成了对于Bean属性值的设置。
Aware注入
接下来是Aware注入。在使用Spring的时候我们将自己的Bean实现BeanNameAware接口、BeanFactoryAware接口等,依赖容器帮我们注入当前Bean的名称或者Bean工厂,其代码实现先追溯到上面doCreateBean方法的42行initializeBean方法:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
看一下上面第5行的实现:
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
看到这里判断,如果bean是BeanNameAware接口的实现类会调用setBeanName方法、如果bean是BeanClassLoaderAware接口的实现类会调用setBeanClassLoader方法、如果是BeanFactoryAware接口的实现类会调用setBeanFactory方法,注入对应的属性值。
调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
上面initializeBean方法再看16行其实现:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
遍历每个BeanPostProcessor接口实现,调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,这个接口的调用时机之后会总结,这里就代码先简单提一下。
调用初始化方法
initializeBean方法的20行,调用Bean的初始化方法,看一下实现:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
看到,代码做了两件事情:
1、先判断Bean是否InitializingBean的实现类,是的话,将Bean强转为InitializingBean,直接调用afterPropertiesSet()方法
2、尝试去拿init-method,假如有的话,通过反射,调用initMethod
因此,两种方法各有优劣:使用实现InitializingBean接口的方式效率更高一点,因为init-method方法是通过反射进行调用的;从另外一个角度讲,使用init-method方法之后和Spring的耦合度会更低一点。具体使用哪种方式调用初始化方法,看个人喜好。
调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
最后一步,initializeBean方法的29行:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
同样遍历BeanPostProcessor,调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法。因此对于BeanPostProcessor方法总结一下:
1、在初始化每一个Bean的时候都会调用每一个配置的BeanPostProcessor的方法
2、在Bean属性设置、Aware设置后调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
3、在初始化方法调用后调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
注册需要执行销毁方法的Bean
接下来看一下最上面doCreateBean方法的第83行registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd)这一句,完成了创建Bean的最后一件事情:注册需要执行销毁方法的Bean。
看一下方法的实现:
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
else {
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
}
}
其中第3行第一个判断为必须不是prototype(原型)的,第二个判断requiresDestruction方法的实现为:
1 protected boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
2 return (bean != null &&
3 (bean instanceof DisposableBean || mbd.getDestroyMethodName() != null ||
4 hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors()));
5 }
要注册销毁方法,Bean需要至少满足以下三个条件之一:
(1)Bean是DisposableBean的实现类,此时执行DisposableBean的接口方法destroy()
(2)Bean标签中有配置destroy-method属性,此时执行destroy-method配置指定的方法
(3)当前Bean对应的BeanFactory中持有DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,此时执行DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的接口方法postProcessBeforeDestruction
在满足上面三个条件之一的情况下,容器便会注册销毁该Bean,注册Bean的方法很简单,见registerDisposableBean方法实现:
1 public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
2 synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
3 this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
4 }
5 }
容器销毁的时候,会遍历disposableBeans,逐一执行销毁方法。
流程总结
本文和上篇文章分析了Spring Bean初始化的步骤,最后用一幅图总结一下Spring Bean初始化的流程:
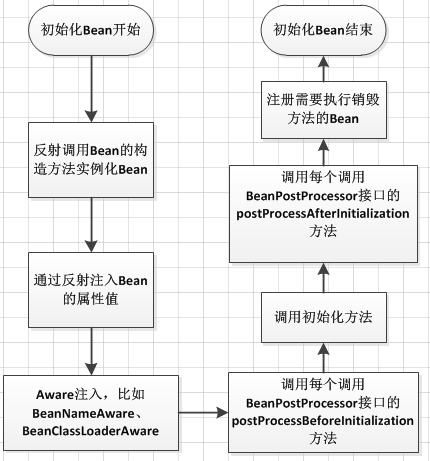
图只是起梳理流程作用,抛砖引玉,具体代码实现还需要网友朋友们照着代码自己去一步一步分析。





