简介
mock是模拟对象,用于模拟真实对象的行为。
Powermock主要用于打桩。比如:方法A的参数需要传入实例B,方法A需要调用B的某个方法B.C()。方法C因为耗时长或者根本没有实现或者其他不方便在单元测试中实现等原因,需要伪造返回,此时Powermock即可派上用场。
PowerMock扩展了EasyMock和Mockito框架,增加了对static和final方法mock支持等功能。这里主要基于PowerMock Mockito API进行介绍。
PowerMock支持JUnit和TestNG,这里基于JUnit。
介绍
英文原版书籍下载:https://bitbucket.org/xurongzhong/python-chinese-library/downloadss。
精品文章推荐:
性能测试艺术
Java单元测试之模拟利器-使用PowerMock进行Mock测试
安装
下载地址:https://github.com/jayway/powermock/wiki/Downloads。下载” Mockito and JUnit including dependencies”版本。当前版本为”powermock-mockito-junit-1.6.3.zip“。
IntelliJ IDEA的设置如下:
右击工程,选择“Open Module Settings”
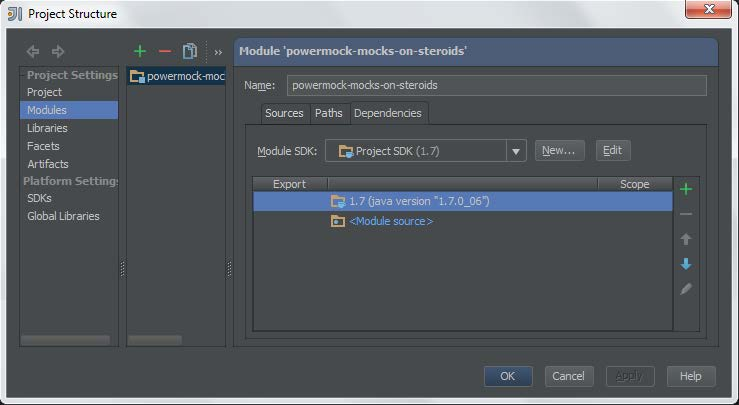
按下“ALT + Insert”,选择“Jars or directories…”, 插入jar包:
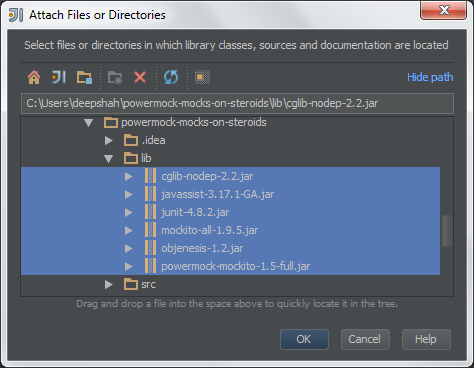
点击OK。
在”Module Settings”对话框中点击“Sources”标签,右击右边底部面板,选择“New Folder…”, 命名为test。
在”Module Settings”对话框中选择test,标识为Test Sources,关闭”Module Settings”对话框。
Eclipse中只需要上述jar包放在工程下的lib目录即可。
Maven在pom.xml添加如下内容:
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-api-mockito</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
快速入门
下面创建EmployeeController类用于给Employee类执行Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD)。实际工作由EmployeeService完成。getProjectedEmployeeCount方法预计公司员工每年增加20%,并返回近似取整。
public class EmployeeController {
private EmployeeService employeeService;
public EmployeeController(EmployeeService employeeService) {
this.employeeService = employeeService;
}
public int getProjectedEmployeeCount() {
final int actualEmployeeCount = employeeService.getEmployeeCount();
return (int) Math.ceil(actualEmployeeCount * 1.2);
}
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
}
}
public class EmployeeService {
public int getEmployeeCount() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
由于getEmployeeCount等方法没有真正实现,我们需要mock:
public class Employee {
}
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
public class EmployeeControllerTest {
@Test
public void shouldReturnProjectedCountOfEmployeesFromTheService() {
EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class);
PowerMockito.when(mock.getEmployeeCount()).thenReturn(8);
EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
assertEquals(10, employeeController.getProjectedEmployeeCount());
}
@Test
public void
shouldInvokeSaveEmployeeOnTheServiceWhileSavingTheEmployee() {
EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class);
EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
Employee employee = new Employee();
employeeController.saveEmployee(employee);
Mockito.verify(mock).saveEmployee(employee);
}
}
注意如果上述代码出现莫名其妙的错误,建议先确认所有文件已经保存,再不行重启Eclipse。
上面的saveEmployee(Employee)没有返回值,我们只需要用verify确认有调用即可。如果注释掉employeeController.saveEmployee(employee);就会有如下报错:
Wanted but not invoked:
employeeService.saveEmployee(
Employee@51081592
);
-> at EmployeeControllerTest.shouldInvokeSaveEmployeeOnTheServiceWhileSavingTheEmployee(EmployeeControllerTest.java:27)
Actually, there were zero interactions with this mock.
at EmployeeControllerTest.shouldInvokeSaveEmployeeOnTheServiceWhileSavingTheEmployee(EmployeeControllerTest.java:27)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:86)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:459)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:675)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:382)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:192)
另外有个非常用的MockSettings功能,用于设置mock名、实现额外接口(参见https://groups.google.com/forum/?fromgroups=#!topic/mockito/YM5EF0x90_4)、开启详细日志、注册listener用于mock时通知消息调用。比如:
EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class, Mockito.withSettings().name("EmployeeServiceMock").verboseLogging());
从上面例子可以看出,mock常用于参数,如果是方法内部的局部变量偏多、逻辑过于复杂,mock将是比较痛苦的过程,甚至无从下手。
注意:Eclipse如果看不到lib,请选中工程目录,按F5刷新。lib中的每个jar,需要右键点击,选择”Build Path”->”Add to Build Path”, 添加完毕的效果图如下:

模拟静态方法
修改类Employee:
public class Employee {
public static int count() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
修改EmployeeService类的方法:
public int getEmployeeCount() {
return Employee.count();
}
新建EmployeeServiceTest类:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(Employee.class)
public class EmployeeServiceTest {
@Test
public void shouldReturnTheCountOfEmployeesUsingTheDomainClass() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(Employee.count()).thenReturn(900);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
assertEquals(900, employeeService.getEmployeeCount());
}
}
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)语句告诉JUnit用PowerMockRunner来执行测试。
@PrepareForTest(Employee.class)语句告诉PowerMock准备Employee类进行测试。适用于模拟final类或有final, private, static, native方法的类。
注意这里使用的是mockStatic而不是上面的mock。
下面我们模拟下返回void的静态方法。在Employee添加加薪方法:
public static void giveIncrementOf(int percentage) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
EmployeeService添加相应方法:
public boolean giveIncrementToAllEmployeesOf(int percentage) {
try{
Employee.giveIncrementOf(percentage);
return true;
} catch(Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
修改EmployeeServiceTest类
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(Employee.class)
public class EmployeeServiceTest {
@Test
public void shouldReturnTrueWhenIncrementOf10PercentageIsGivenSuccessfully() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(Employee.class);
Employee.giveIncrementOf(10);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
assertTrue(employeeService.giveIncrementToAllEmployeesOf(10));
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnFalseWhenIncrementOf10PercentageIsNotGivenSuccessfully() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.doThrow(new IllegalStateException()).when(Employee.class);
Employee.giveIncrementOf(10);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
assertFalse(employeeService.giveIncrementToAllEmployeesOf(10));
}
}
PowerMockito.doNothing方法告诉PowerMock下一个方法调用时什么也不做。
PowerMockito.doThrow方法告诉PowerMock下一个方法调用时产生异常。
PowerMock使用自定义类加载器和字节码操作来模拟静态方法。对于实例中没有mock的方法,也有默认返回值,比如返回int类型的方法,默认返回0。
PowerMockito.doNothing和PowerMockito.doThrow的语法可用于实例方法。
先在Employee类添加方法save:
public void save() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
创建测试EmployeeTest 类:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
public class EmployeeTest {
@Test()
public void shouldNotDoAnythingIfEmployeeWasSaved() {
Employee employee = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(employee).save();
try {
employee.save();
} catch(Exception e) {
fail("Should not have thrown an exception");
}
}
@Test(expected = IllegalStateException.class)
public void shouldThrowAnExceptionIfEmployeeWasNotSaved() {
Employee employee = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.doThrow(new IllegalStateException()).when(employee).save();
employee.save();
}
}
注意这里doThrow和doNothing方法不会对下一行产生影响。
验证方法调用
验证断言方法是否调用。
修改EmployeeService类的saveEmployee方法。
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
if(employee.isNew()) {
employee.create();
return;
}
employee.update();
}
修改Employee类,新增如下方法:
public boolean isNew() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void update() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void create() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public static void giveIncrementOf(int percentage) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
在EmployeeServiceTest类中新增shouldCreateNewEmployeeIfEmployeeIsNew方法, 并新增导入import org.mockito.Mockito;:
@Test
public void shouldCreateNewEmployeeIfEmployeeIsNew() {
Employee mock = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(mock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
employeeService.saveEmployee(mock);
Mockito.verify(mock).create();
Mockito.verify(mock, Mockito.never()).update();
}
Mockito.verify(mock).create()验证调用了create方法。 Mockito.verify(mock, Mockito.never()).update();验证没有调用update方法。
下面验证静态方法,在EmployeeServiceTest类添加shouldInvoke_giveIncrementOfMethodOnEmployeeWhileGivingIncrement方法:
<code> </code>
@Test
public void shouldInvoke_giveIncrementOfMethodOnEmployeeWhileGivingIncrement() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(Employee.class);
Employee.giveIncrementOf(9);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
employeeService.giveIncrementToAllEmployeesOf(9);
PowerMockito.verifyStatic();
Employee.giveIncrementOf(9);
}
同样,静态验证也要分两步走。
其他验证模式可以验证调用次数:
- Mockito.times(int n) : This verification mode asserts that the mocked method was invoked exactly ‘n’ times
- Mockito.atLeastOnce() : This verification mode asserts that the mocked method was invoked at least once
- Mockito.atLeast(int n) : This verification mode asserts that the mocked method was invoked at least ‘n’ times
- Mockito.atMost(int n) : This verification mode asserts that the mocked method was invoked at most ‘n’ times
使用Mockito.inOrder还可以验证调用的顺序,注意要导入import org.mockito.InOrder;
@Test
public void shouldInvokeIsNewBeforeInvokingCreate() {
Employee mock = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(mock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
employeeService.saveEmployee(mock);
InOrder inOrder = Mockito.inOrder(mock);
inOrder.verify(mock).isNew();
Mockito.verify(mock).create();
Mockito.verify(mock, Mockito.never()).update();
}
模拟final类或方法
新增EmployeeIdGenerator类:
public final class EmployeeIdGenerator {
public final static int getNextId() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
在Employee类新增方法:
public void setEmployeeId(int nextId) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
修改EmployeeService类的saveEmployee方法:
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
if(employee.isNew()) {
employee.setEmployeeId(EmployeeIdGenerator.getNextId());
employee.create();
return;
}
employee.update();
}
修改EmployeeServiceTest类:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(EmployeeIdGenerator.class)
public class EmployeeServiceTest {
@Test
public void shouldGenerateEmployeeIdIfEmployeeIsNew() {
Employee mock = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(mock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
PowerMockito.mockStatic(EmployeeIdGenerator.class);
PowerMockito.when(EmployeeIdGenerator.getNextId()).thenReturn(90);
EmployeeService employeeService = new
EmployeeService();
employeeService.saveEmployee(mock);
PowerMockito.verifyStatic();
EmployeeIdGenerator.getNextId();
Mockito.verify(mock).setEmployeeId(90);
Mockito.verify(mock).create();
}
}
可见final和static的在类头部处理方法类似,两者可以基本归为一类。
其他java mock框架大多基于代理模式,参见https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_pattern#Example 。这种方式严重依赖子类及方法可以重载。所以不能模拟final和static。
处理构造方法
现在创建新职员的时候要发送欢迎邮件。
新增类WelcomeEmail:
public class WelcomeEmail {
public WelcomeEmail(final Employee employee, final String message) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void send() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
修改EmployeeService类的saveEmployee方法:
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
if(employee.isNew()) {
employee.setEmployeeId(EmployeeIdGenerator.getNextId());
employee.create();
WelcomeEmail emailSender = new WelcomeEmail(employee,
"Welcome to Mocking with PowerMock How-to!");
emailSender.send();
return;
}
employee.update();
}
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({EmployeeIdGenerator.class, EmployeeService.class})
public class EmployeeServiceTest {
@Test
public void shouldSendWelcomeEmailToNewEmployees()throws Exception {
Employee employeeMock =PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(employeeMock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
PowerMockito.mockStatic(EmployeeIdGenerator.class);
WelcomeEmail welcomeEmailMock = PowerMockito.mock(WelcomeEmail.class);
PowerMockito.whenNew(WelcomeEmail.class).withArguments(employeeMock, "Welcome to Mocking with PowerMock How-to!").thenReturn(welcomeEmailMock);
EmployeeService employeeService = new EmployeeService();
employeeService.saveEmployee(employeeMock);
PowerMockito.verifyNew(WelcomeEmail.class).withArguments(employeeMock, "Welcome to Mocking with PowerMock How-to!");
Mockito.verify(welcomeEmailMock).send();
}
}
注意PowerMockito.verifyNew的第2个参数支持前面提到的验证模式。PowerMockito.whenNew().withArguments(…).thenReturn()是对构造方法的mock模式,PowerMockito.verifyNew().withArguments()是验证模式。
参数匹配
PowerMock使用equals方法验证参数。matcher可更加灵活的处理参数。
为EmployeeController类添加如下方法:
public Employee findEmployeeByEmail(String email) {
return employeeService.findEmployeeByEmail(email);
}
public boolean isEmployeeEmailAlreadyTaken(String email) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
return employeeService.employeeExists(employee);
}
为EmployeeService类添加如下方法:
public Employee findEmployeeByEmail(String email) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean employeeExists(Employee employee) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
为EmployeeControllerTest类新增测试
@Test
public void shouldFindEmployeeByEmail() {
final EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class);
final Employee employee = new Employee();
PowerMockito.when(mock.findEmployeeByEmail(Mockito.startsWith("deep"))).thenReturn(employee);
final EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
assertSame(employee, employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@gitshah.com"));
assertSame(employee, employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@packtpub.com"));
assertNull(employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("noreply@packtpub.com"));
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnNullIfNoEmployeeFoundByEmail() {
final EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class);
PowerMockito.when(mock.findEmployeeByEmail(Mockito.anyString())).thenReturn(null);
final EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
assertNull(employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@gitshah.com"));
assertNull(employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@packtpub.com"));
assertNull(employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("noreply@packtpub.com"));
}
后面还有个基于argThat例子,因为没有搞到源码,意思暂时没有揣度出来。先不涉及。
另外其他类似的内置匹配器如下:Mockito.eq、Mockito.matches、Mockito.any(anyBoolean , anyByte , anyShort , anyChar , anyInt ,anyLong , anyFloat , anyDouble , anyList , anyCollection , anyMap , anySet等等)、Mockito.isNull、Mockito.isNotNull、Mockito.endsWith、Mockito.isA。
回答(Answer)
在某些边缘的情况下不可能通过简单地通过PowerMockito.when().thenReturn()模拟,这时可以使用Answer接口。
在EmployeeControllerTest类中增加如下方法:
import org.mockito.stubbing.Answer;
public class EmployeeControllerTest {
@Test
public void shouldFindEmployeeByEmailUsingTheAnswerInterface() {
final EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class);
final Employee employee = new Employee();
PowerMockito.when(mock.findEmployeeByEmail(Mockito.anyString())).then(new Answer<Employee>() {
public Employee answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable {
final String email = (String) invocation.getArguments()[0];
if(email == null) return null;
if(email.startsWith("deep")) return employee;
if(email.endsWith("packtpub.com")) return employee;
return null;
}
});
final EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
assertSame(employee, employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@gitshah.com"));
assertSame(employee, employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("deep@packtpub.com"));
assertNull(employeeController.findEmployeeByEmail("hello@world.com"));
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnCountOfEmployeesFromTheServiceWithDefaultAnswer() {
EmployeeService mock = PowerMockito.mock(EmployeeService.class, new Answer() {
public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) {
return 10;
}
});
EmployeeController employeeController = new EmployeeController(mock);
assertEquals(12, employeeController.getProjectedEmployeeCount());
}
}
Answer接口指定执行的action和返回值执。 Answer的参数是InvocationOnMock的实例,支持:
- callRealMethod():调用真正的方法
- getArguments():获取所有参数
- getMethod():返回mock实例调用的方法
- getMock():获取mock实例
第一个测试方法根据不同情况构造不同返回。第2个测试方法设定调用返回的默认值。
使用spy进行部分模拟
现在调整类EmployeeService,拆分saveEmployee为方法:saveEmployee和createEmployee:
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
if(employee.isNew()) {
createEmployee(employee);
return;
}
employee.update();
}
void createEmployee(Employee employee) {
employee.setEmployeeId(EmployeeIdGenerator.getNextId());
employee.create();
WelcomeEmail emailSender = new WelcomeEmail(employee,
"Welcome to Mocking with PowerMock How-to!");
emailSender.send();
}
EmployeeServiceTest类添加测试方法shouldInvokeTheCreateEmployeeMethodWhileSavingANewEmployee:
@Test
public void shouldInvokeTheCreateEmployeeMethodWhileSavingANewEmployee() {
final EmployeeService spy = PowerMockito.spy(new EmployeeService());
final Employee employeeMock = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(employeeMock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(spy).createEmployee(employeeMock);
spy.saveEmployee(employeeMock);
Mockito.verify(spy).createEmployee(employeeMock);
}
注意spy只能使用PowerMockito.doNothing()/doReturn()/doThrow()。
模拟私有方法
现在我们修改EmployeeService.createEmployee为private,在EmployeeServiceTest类添加如下方法:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({EmployeeIdGenerator.class, EmployeeService.class})
public class EmployeeServiceTest {
@Test
public void shouldInvokeTheCreateEmployeeMethodWhileSavingANewEmployee() throws Exception {
final EmployeeService spy = PowerMockito.spy(new EmployeeService());
final Employee employeeMock = PowerMockito.mock(Employee.class);
PowerMockito.when(employeeMock.isNew()).thenReturn(true);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(spy, "createEmployee", employeeMock);
spy.saveEmployee(employeeMock);
PowerMockito.verifyPrivate(spy).invoke("createEmployee", employeeMock);
}
}
模拟私有方法还有另外一种相对较复杂的方法,这里不做介绍了。
查看封装内容
添加 Department类
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Department {
private List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
private long maxSalaryOffered;
public void addEmployee(final Employee employee) {
employees.add(employee);
updateMaxSalaryOffered();
}
/**
* The private method that keeps track of
* max salary offered by this department.
*/
private void updateMaxSalaryOffered() {
maxSalaryOffered = 0;
for (Employee employee : employees) {
if(employee.getSalary() > maxSalaryOffered) {
maxSalaryOffered = employee.getSalary();
}
}
}
}
修改Employee类的如下方法:
public long getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int i) {
salary = i;
}
新建DepartmentTest类,添加如下测试方法:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.powermock.reflect.Whitebox;
public class DepartmentTest {
@Test
public void shouldVerifyThatNewEmployeeIsAddedToTheDepartment() {
final Department department = new Department();
final Employee employee = new Employee();
department.addEmployee(employee);
final List<Employee> employees = Whitebox.getInternalState(department, "employees");
assertTrue(employees.contains(employee));
}
@Test
public void shouldAddNewEmployeeToTheDepartment() {
final Department department = new Department();
final Employee employee = new Employee();
final ArrayList<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Whitebox.setInternalState(department, "employees", employees);
department.addEmployee(employee);
assertTrue(employees.contains(employee));
}
@Test
public void shouldVerifyThatMaxSalaryOfferedForADepartmentIsCalculatedCorrectly() throws Exception
{
final Department department = new Department();
final Employee employee1 = new Employee();
final Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee1.setSalary(60000);
employee2.setSalary(65000);
//Adding two employees to the test employees list.
final ArrayList<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
employees.add(employee1);
employees.add(employee2);
Whitebox.setInternalState(department, "employees", employees);
Whitebox.invokeMethod(department,"updateMaxSalaryOffered");
final long maxSalary = Whitebox.getInternalState(department, "maxSalaryOffered");
assertEquals(65000, maxSalary);
}
}
Whitebox.getInternalState(department, “employees”)类似堆栈,查看变量的值。Whitebox.setInternalState(department, “employees”,
employees)设置变量的值。 Whitebox.invokeMethod(department, “updateMaxSalaryOffered”)调用方法。
更多参考:http://powermock.googlecode.com/svn/docs/powermock-1.5/apidocs/org/powermock/reflect/Whitebox.html。
ads_sms中测试手机号码发送短信
package com.oppo.os.ads.sms.sevice;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.powermock.reflect.Whitebox;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:dubbo/ads-sms-svc.xml")
public class SmsTaskTest {
@Autowired
SmsTask svc;
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void checkLimitOk() throws Exception {
System.out.println("initAccUser");
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(svc,"checkLimit", 6, "13246680798", 3, 20160121, 20160121);
assertEquals(true, result);
}
@Test
public void checkLimitFail() throws Exception {
System.out.println("initAccUser");
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(svc,"checkLimit", 0, "13246680998", 3, 20160121, 20160121);
assertEquals(false, result);
}
}
ads_ad 中的pom.xml配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-api-mockito</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4-rule</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-classloading-xstream</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
测试文件:
package com.oppo.os.ads.ad.cpd.app.service;
import org.junit.Rule;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.rule.PowerMockRule;
import org.powermock.reflect.Whitebox;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import static org.mockito.Matchers.*;
import com.oppo.os.ads.ad.cpd.app.entity.AdsAdBid;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:dubbo/ad-cpd-app-svc.xml")
public class AdsAdAppBidSrvTest {
//@Rule
//public PowerMockRule rule = new PowerMockRule();
@Autowired
AdsAdAppBidSrv appSrvImpl;
@Test
public void testAccOutDayBudgetString() {
appSrvImpl.accOutDayBudget("2839488");
}
@Test
public void testAccOutDayBudgetInt() {
appSrvImpl.accOutDayBudget(2839488);
}
@Test
public void testOutDayBudget() {
appSrvImpl.outDayBudget(5160);
}
@Test
public void testBalanceInsufficientString() {
appSrvImpl.balanceInsufficient("2839488");
}
@Test
public void testBalanceInsufficientLong() {
appSrvImpl.balanceInsufficient(2839488);
}
@Test
public void testAddAd() {
AdsAdBid bid = new AdsAdBid();
bid.setId(5160L);
appSrvImpl.addAd(bid);
}
@Test
public void testUpdateAd() {
AdsAdBid bid = new AdsAdBid();
bid.setId(5160L);
bid.setName("789798");
appSrvImpl.updateAd(bid);
}
@Test
public void testStartAd() {
appSrvImpl.startAd(5160);
}
@Test
public void testPauseAd() {
AdsAdBid bid = new AdsAdBid();
bid.setId(5160L);
appSrvImpl.pauseAd(bid);
}
@Test
public void testDeleteAdCache() throws Exception {
Whitebox.invokeMethod(appSrvImpl,"deleteAdCache", "1001");
}
}
禁用非预期行为
新增类BaseEntity:
public class BaseEntity {
static {
String x = null;
x.toString();
}
public BaseEntity() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected void performAudit(String auditInformation) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
修改类Department:
public class Department extends BaseEntity {
private int departmentId;
private String name;
public Department(int departmentId) {
super();
this.departmentId = departmentId;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
super.performAudit(this.name);
}
protected void performAudit(String auditInformation) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Object getDepartmentId() {
return departmentId;
}
public Object getName() {
return name;
}
}
修改类DepartmentTest:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.SuppressStaticInitializationFor;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(Department.class)
@SuppressStaticInitializationFor("BaseEntity")
public class DepartmentTest {
@Test
public void shouldSuppressTheBaseConstructorOfDepartment() {
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.constructor(BaseEntity.class));
assertEquals(10, new Department(10).getDepartmentId());
}
@Test
public void shouldSuppressThePerformAuditMethodOfBaseEntity() {
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.constructor(BaseEntity.class));
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.method(BaseEntity.class, "performAudit", String.class));
final Department department = new Department(18);
department.setName("Mocking with PowerMock");
assertEquals("Mocking with PowerMock", department.getName());
}
@Test
public void shouldSuppressTheInitializerForBaseEntity() {
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.constructor(BaseEntity.class));
assertNotNull(new Department(18));
}
}
注意测试代码并未试验成功。
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.constructor(BaseEntity.class));表示禁用BaseEntity的构造函数。PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.constructor(BaseEntity.class, String.class, Integer.class))后面表示带字符串和整数参数。
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.method(BaseEntity.class, “performAudit”, String.class))表示禁用BaseEntity的performAudit方法。
@SuppressStaticInitializationFor(“BaseEntity”)表示禁用BaseEntity的静态初始化。注意引号部分通常需要全名,比如”com.gitshah.powermock.BaseEntity”。
PowerMockito.suppress(PowerMockito.field(BaseEntity.class,”identifier”)):禁用域。
参考资料
简明教程: https://github.com/jayway/powermock
https://github.com/jayway/powermock/wiki/MockitoUsage
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-powermock/
书籍:Instant Mock Testing with PowerMock





